Osgood-Schlatter disease: Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
Understanding the knee condition that often affects sporting teenagers.
What is Osgood Schlatters?
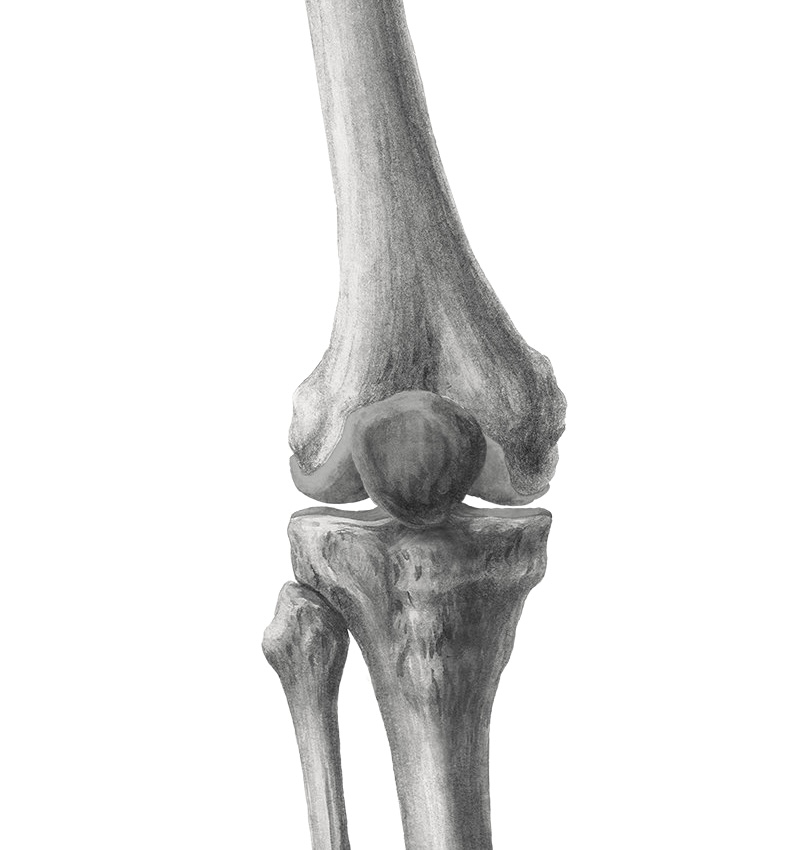
Osgood-Schlatter disease is an overuse condition or injury of the knee that causes a painful bump and swelling on the shinbone below the knee.
Common Symptoms:
- Pain focused on the point of the knee, which is worsened after exercise
- Pain with kneeling
- Visible lump at the base of the knee cap
- Common with very active teenagers
Why does it occur?
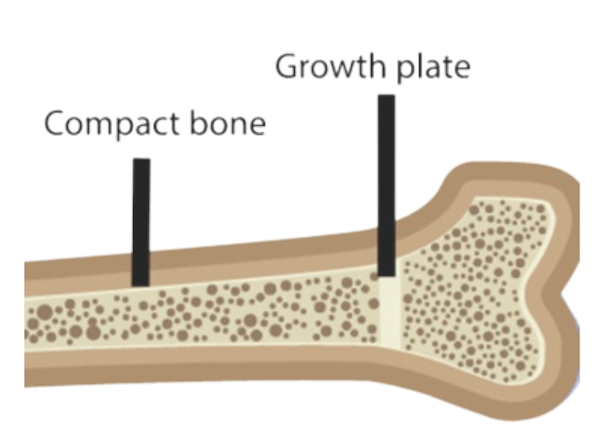
When you’re growing, the ends of your bones are not yet hardened, this area is called the growth plate.
This is made out of cartilage, which is softer than bone.
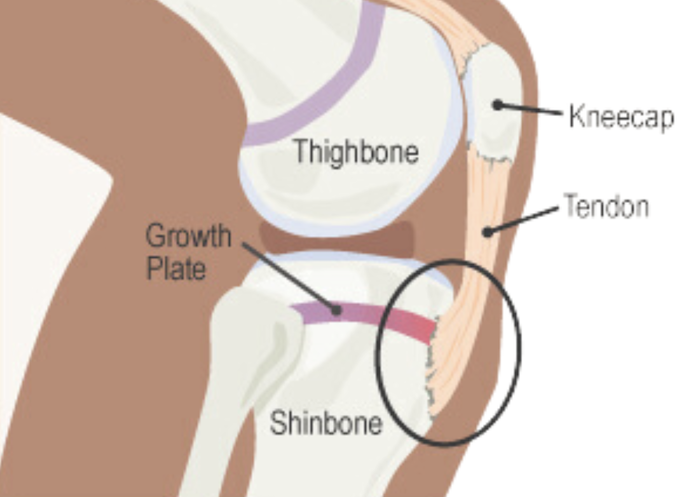
For individuals who have not yet stopped growing, this repeated stress can cause the growth plate to soften, swell and partially open – leading to the visible lump at the top of the shin that is painful.
TAKEAWAYS
Long-term outcomes are good
The pain will generally resolve once growing stops.
You can still be active
Reducing the load on the knee will help manage the condition but complete rest is generally not advised for Osgood Schlatters.
Corrective Exercises
Apart from icing + massage for pain, corrective exercise can further assist with recovery and keep pain levels low.
Physiotherapists can help
A physiotherapist can diagnose Osgood Schlatters and provide advice on the best management options for you.
EXERCISES FOR Osgood Schlatters?
Single Leg Isometric Knee Extension on WaLL
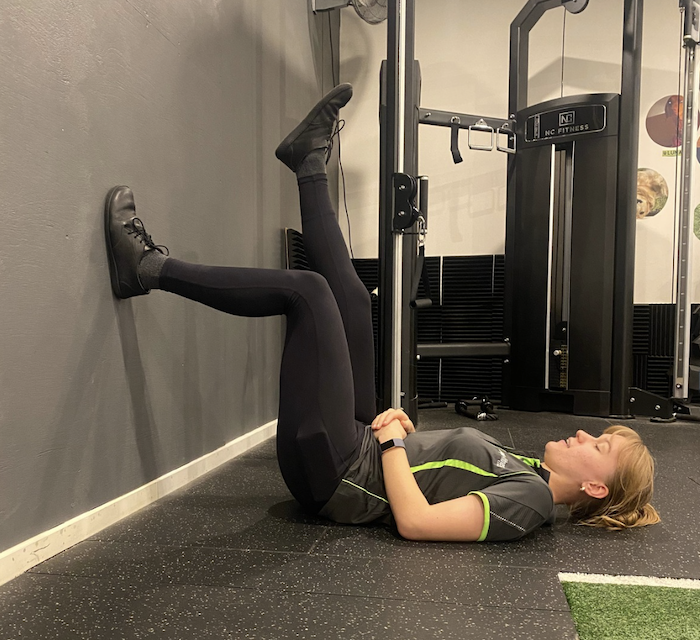

- Lying on your back near a wall
- Place foot on the wall, with knee at 90 degree angle
- Push foot into the wall, trying to extend knee
- Hold for 30-45 secs
Wall Sit
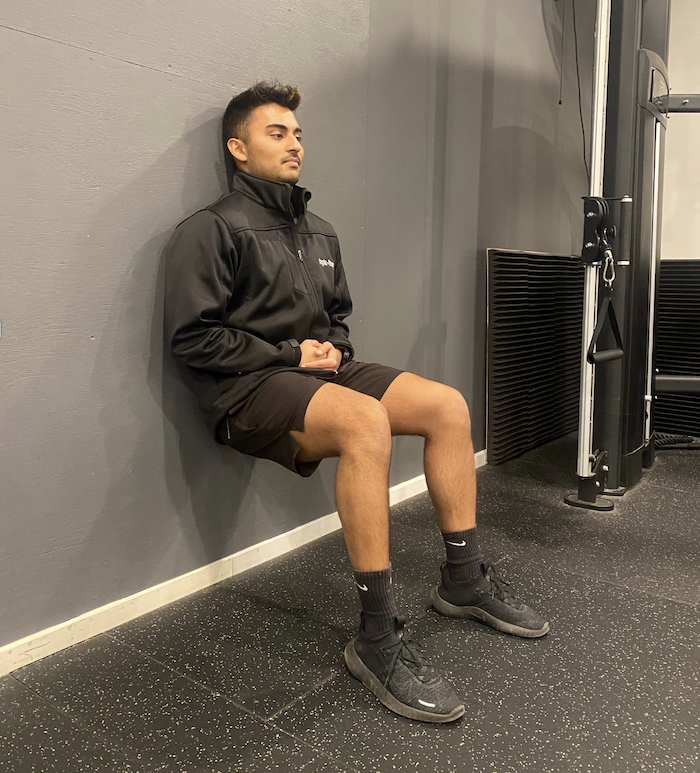

- Start standing with your back on a wall
- Slide yourself down until your knees are at a comfortable angle
- Hold for 30-45 secs
Heels Elevated Squat
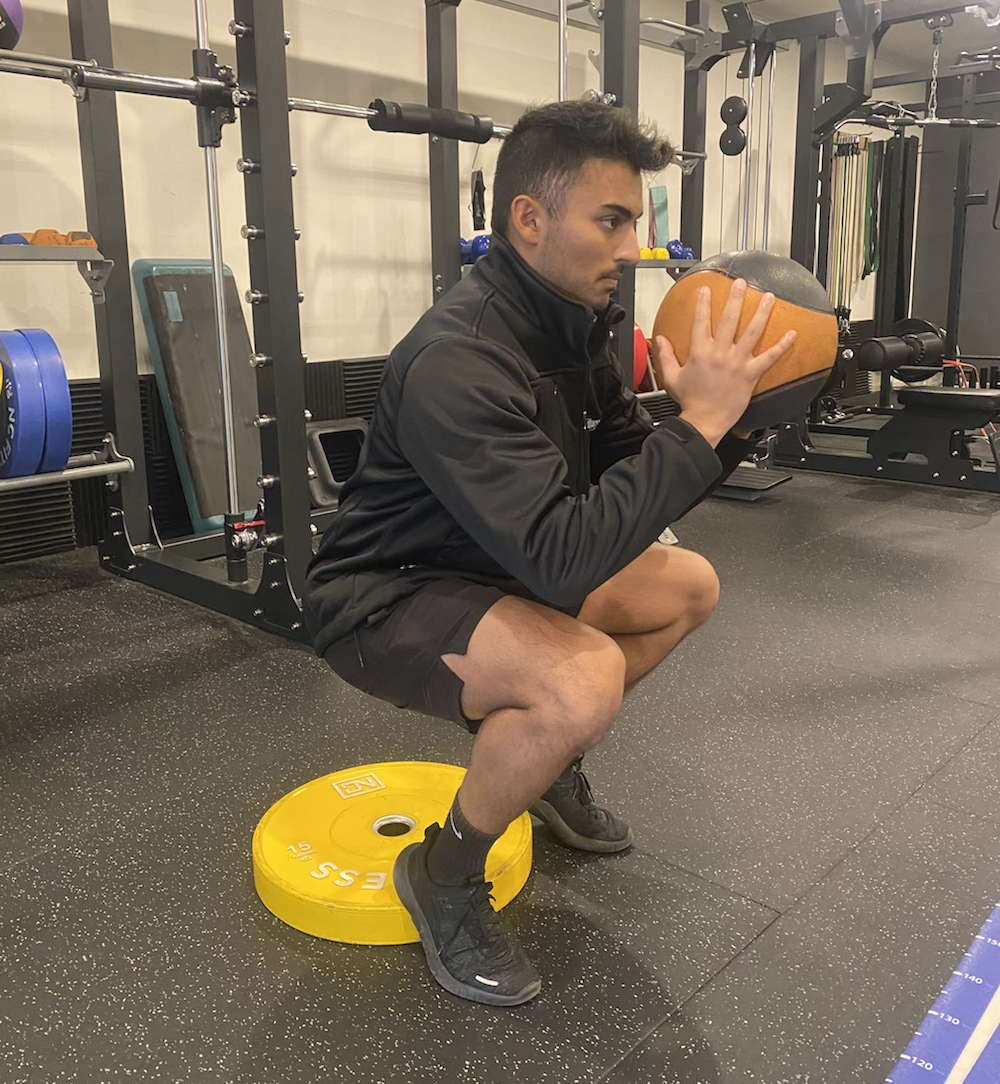

- Stand with your heels on a raised surface
- Squat down as far a comfortable for your knee
- Hold onto extra weight if able
- Complete 8-12 reps
Remember, it’s important to listen to your body and avoid any excessive pain or discomfort. If you experience sharp or prolonged pain, consult with a healthcare professional before continuing.
